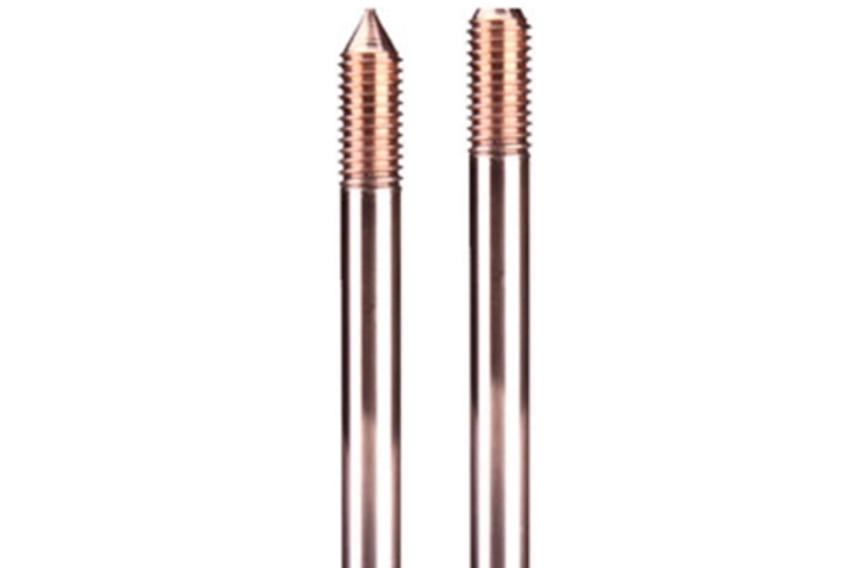
What is a Lightning Protection Grounding Rods?
Lightning protection Grounding Rods, also known as grounding electrodes or grounding grids, are designed to enhance the internal conductivity of grounding conductors and reduce the soil resistivity external to the grounding conductors. These products offer advantages such as simple construction, small land occupation, no environmental pollution, long service life, and low resistance values.

They are widely used in various fields such as communication, power, transportation, finance, petrochemical, and building systems. For example, in communication bureaus (stations), mobile base stations, dispatching rooms, substations, highway facilities, computer rooms, and intelligent communities with strict grounding requirements, this system can form a high-performance grounding system. Copper-clad steel materials, with their good electrical conductivity, high mechanical strength, and especially the copper layer that provides good corrosion resistance, have been widely used in grounding devices. The United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, and other countries have stipulated in their standards that grounding bodies and grounding lines can use copper-clad steel composite materials. In China, the corrosion resistance and reliability of grounding devices have attracted increasing attention, and copper-clad steel composite materials are being used as substitutes.
Classification of Lightning Protection Grounding Rods
1. Copper-plated Grounding Rods: A steel Grounding Rods with a copper layer of more than 0.254mm thickness on the outside is called a copper-plated Grounding Rods, also known as a copper-clad steel Grounding Rods, etc.
2. Galvanized Grounding Rods: A steel bar with a hot-dip galvanizing anti-corrosion treatment on the outside.
3. Pure Copper Grounding Rods: A Grounding Rods made from pure copper material.

When designing a grounding system, we must consider soil conditions to make the best choice. The foundation of grounding system design is accurate measurement of the soil to understand the resistivity of the soil at different soil layers. With this data, we can decide from a technical and economic perspective which grounding system is the best. One important point is that the distance between vertical bars should at least be equal to the length L of the installed bar, but should not exceed 10 meters. With the above conditions, we can be sure that the selected Grounding Rods will be effective for many years.
Soil Conditions
Soil resistivity directly affects the installation method of the grounding system. The following are some factors that affect soil resistivity:
Physical Composition: According to different soil components, the resistivity range can vary from a few ohm-meters to thousands of ohm-meters. It is best to avoid dry, sandy, and rocky soils.
Soil Resistivity:

Soil moisture
Humidity: Increasing the soil’s humidity can quickly reduce its resistivity. In areas with large variations in rainfall, considering the soil’s humidity is very important. Therefore, Grounding Rods should be installed as much as possible below the groundwater level or in a permanent groundwater layer.
Temperature: The change in soil temperature also has a significant impact on resistivity. The effect of temperature on resistivity is shown in the following table (taking sandy soil with a humidity of 15.2% as an example).

Material Selection:
When choosing grounding materials, their corrosion resistance should be considered. We must ensure that the grounding resistance value does not increase over time and due to corrosion. In some sections later in this sample, you can see a comparison of Grounding Rods made from different materials to make the right choice.
Different Geological Conditions:
Choose the appropriate Grounding Rods based on different geological conditions, with the most common being copper-plated Grounding Rods.

Copper-plated Grounding Rods, also known as copper-clad steel Grounding Rods or copper-covered steel Grounding Rods, refer to a grounding electrode made by covering a steel rod with copper through methods such as electroplating or continuous casting, achieving a high degree of combination between copper and steel. According to the type of use, they can be divided into combined-type Grounding Rods or single-rod-type Grounding Rods. Combined-type Grounding Rods consist of a copper-plated grounding rod with threaded ends, a pointed tip, impact-resistant bolts, and connectors. Their advantages include convenient transportation, and they can be made into longer lengths according to construction needs. Single-rod-type Grounding Rods consist of a single copper-plated grounding electrode, which is convenient for construction.
Copper-plated Grounding Rods save copper material and reduce costs compared to pure copper bars, while maintaining the same electrical conductivity and incorporating the hardness of copper. Copper-plated Grounding Rods are mainly used in lightning protection grounding, which can reduce resistance values. When the lightning rod on the top of a building is struck by lightning, the current can be quickly discharged, achieving the effect of lightning protection.
Features and Technical Advantages:

- Unique Manufacturing Process: The cold rolling and hot drawing production process is adopted to achieve a metallurgical bonding between copper and steel. It can be drawn like a single metal without delamination, warping, or cracking.
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: The composite interface is high-temperature melted with no residue, preventing corrosion phenomena at the junction; the surface copper layer is relatively thick (with an average thickness greater than 0.254mm), which is highly resistant to corrosion, extends the service life (greater than 30 years), and reduces the intensity of maintenance work.
- Better Electrical Performance: The outer layer of pure copper material has excellent electrical conductivity, resulting in a much lower inherent resistance value compared to conventional materials.
- Widely Applicable and Safe: The product is suitable for grounding construction under different soil moisture, temperature, pH value, and resistivity conditions.
- Easy and Fast Installation: With a complete set of accessories and convenient installation, using exothermic welding or special connecting hardware, the joints are solid and have good and stable electrical conductivity, which can effectively increase the construction speed.
- Low Construction Cost: Compared to the traditional method of using pure copper grounding rods, the cost is significantly reduced.
Technical Parameters:
- Copper Layer Thickness: ≥0.25mm
- Electrical Resistivity: ≤0.059Ω·mm²/m
- Tensile Strength: ≥500N/mm²
- Corrosion Resistance: After soaking in a 10% nitric acid solution for over 90 hours, the weight loss due to corrosion should not exceed 15%.
- Copper Layer Adhesion: After continuous exposure at a body temperature of 300°C for over one hour followed by rapid cooling, the copper layer should not peel off.
- Copper Layer Ductility: When the copper-plated grounding rod is bent 180°, the copper layer should show no cracks or signs of flaking.
Product Application Range:
Copper-plated grounding rods are used in lightning protection grounding projects for various locations such as petrochemical plants, oil storage depots, power plants, substations, communication base stations, airports, and network server rooms. The electroformed copper grounding rods, when buried deep underground, offer strong protection against both natural corrosion and electrochemical reactions. The grounding rods and grounding network wires are connected using a chemical welding agent, which places the grounding device entirely under the protection of copper, making it a truly maintenance-free grounding device.
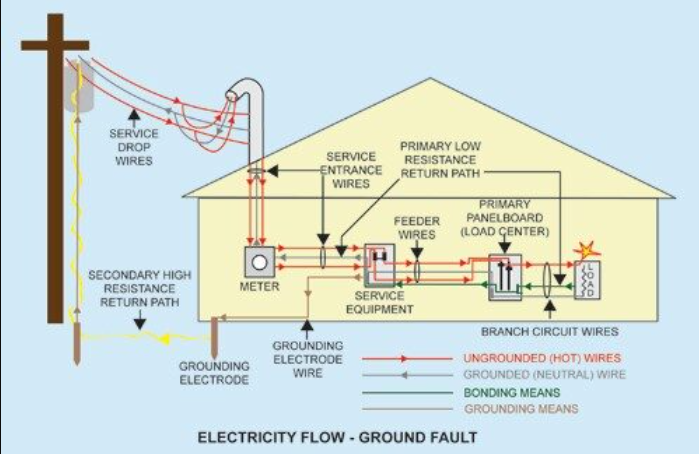
Copper-plated Grounding Rods, according to grounding functions, can generally be divided into:
- Working Ground: Ground bars connected to electronic equipment to achieve equipotential bonding, ensuring the normal operation of the equipment.
- Lightning Protection Ground: Directing the powerful impulse currents in the atmosphere into the ground.
- Protective Ground: Protecting people and animals from electric shock. Copper-plated grounding rods can be used in general environments as well as in special environments such as acidic mud, humidity, salinity, and areas with chemically corrosive media. They are mostly not treated for corrosion protection because the content of active ions in the soil is one of the factors affecting the grounding resistance. In many soils, the compounds containing active electrolytic ions are relatively scarce, and a simple grounding body alone would not meet the grounding requirements.
[wpforms id=”335″ title=”true” description=”true”]







